Essential Cybersecurity Measures to Secure Industrial Operations
Industrial cybersecurity has become a pillar in protecting critical infrastructure from the escalating threat of cyberattacks. As industries increasingly embrace digital transformation, they rely more heavily on interconnected systems, smart devices, and automated control networks. This growing connectivity, while essential for operational efficiency, also introduces new vulnerabilities that can be exploited by threat actors. Sectors such as energy, manufacturing, transportation, and water utilities—often deemed the backbone of national infrastructure—are especially at risk.
A successful cyberattack on these systems could result in not just financial loss or operational disruption, but also public safety hazards and national security implications. Therefore, ensuring the resilience and security of industrial systems is now a top priority for both organizations and governments around the world. Implementing robust industrial cybersecurity strategies is critical for monitoring threats, mitigating risks, and maintaining the continuity of essential services.
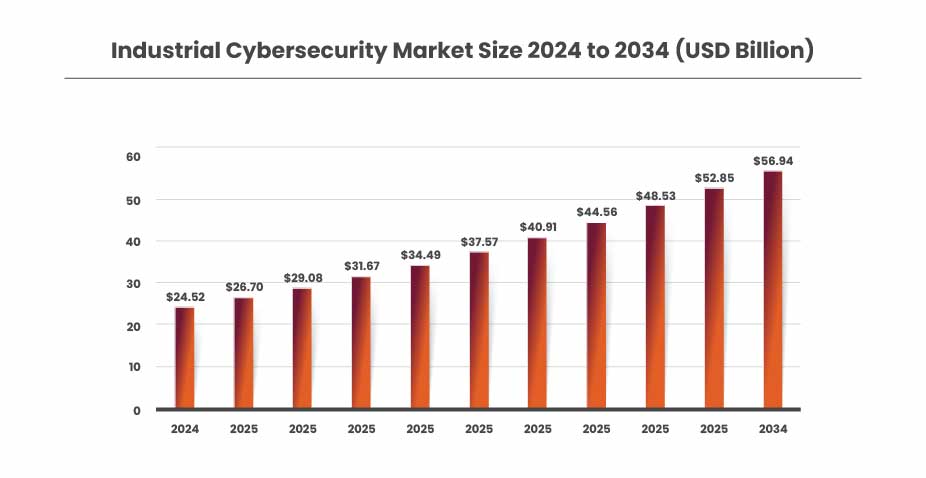
Industrial Cyber Security Market Size
The global industrial cybersecurity market was valued at USD 24.52 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to around USD 56.94 billion by 2034, rising from USD 26.70 billion in 2025. This growth reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.79% between 2025 and 2034. The market’s expansion is primarily fueled by rising investments and the continuous advancement of robust cybersecurity infrastructures across industrial sectors.
What is Industrial Cybersecurity?
Industrial cybersecurity refers to the strategies, technologies, and practices used to protect the computer systems, networks, and data that power critical infrastructure in sectors like energy, manufacturing, transportation, and healthcare. As industries grow more digitized, the risk of cyber threats increases, making it essential to implement strong access controls, conduct regular risk assessments, and establish incident response plans. These measures help prevent unauthorized access, system disruption, and potential disasters, ensuring the resilience and security of essential services.
Get in!
Join our weekly newsletter and stay updated
Why is Industrial Cyber Security Essential?
A successful cyberattack on critical infrastructure can cause severe consequences such as service interruptions, financial damage, reputational harm, and even loss of life. The ripple effects extend beyond the targeted organization, disrupting everyday life and the functioning of society as a whole. For instance, if a cyber attacker were to gain unauthorized access to a power plant’s control systems, it could lead to widespread disruption in transportation, manufacturing, and healthcare services. The resulting economic and social impact would be profound, causing chaos and distress on a large scale.
Given the increasing sophistication and frequency of cyber threats, it is imperative for organizations to prioritize cybersecurity to protect their operations and ensure public safety. Investing in cybersecurity is not only a responsibility but a critical necessity in today’s digital landscape. Additionally, cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires continuous effort. As technology evolves, so do cyberattack methods. Organizations must regularly update their defenses, stay informed about emerging threats, and collaborate with industry experts and peers to maintain a proactive security posture and stay ahead of potential attackers.
Book Your Free Cybersecurity Consultation Today!
CERT-In Cybersecurity Measures for Industrial Operations
The Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) has reported a rise in cyber threats, including ransomware attacks, DDoS incidents, website defacements, data breaches, and malware infections. Whether these threats occur individually or in combination, they pose a serious risk to the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of services.
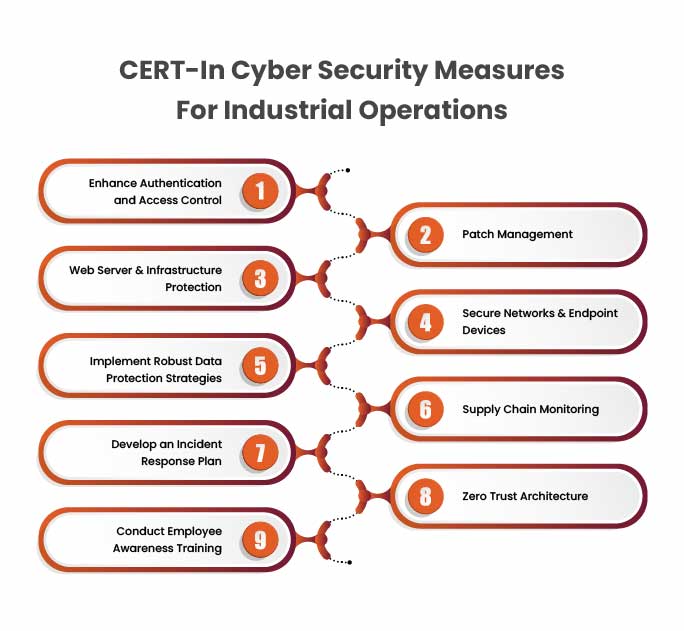
Enhance Authentication Access Control
- Enforce the use of strong, complex, and unique passwords for all services.
- Secure accounts with Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to limit access based on job functions.
Patch Management
- Keep operating systems, applications, and security tools up to date.
- Use automated patching tools to maintain system integrity.
Protect Web Servers & Infrastructure
- Conduct regular scans of web servers and infrastructure to identify open ports and vulnerabilities.
- Remove or secure outdated, unused, or unmaintained web applications and systems.
- Quickly detect and recover from website defacement incidents.
- Utilize web application firewalls to block malicious traffic.
Secure Networks and Endpoints
- Set up firewalls to properly manage incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Encrypt data during storage and transmission to prevent unauthorized access.
- Use email filters to stop phishing attacks and harmful attachments.
- Install antivirus and anti-malware tools to detect and eliminate threats.
Adopt Strong Data Protection Practices
- Perform regular offline backups to reduce ransomware impact.
- Test backup systems frequently to ensure they function when needed.
- Deploy Data Loss Prevention (DLP) technologies to oversee and restrict data movement
Monitor the Supply Chain
Implement continuous oversight of vendor and supplier operations, with special attention to irregularities in software updates or system configurations.
Establish an Incident Response Strategy
- Create a structured response plan to quickly and effectively handle security breaches and cyber incidents.
- Regularly review log files and monitor network activity for signs of suspicious behavior, such as failed login attempts, configuration changes, or unknown device connections.
Adopt Zero Trust Security Model
- Implement a Zero Trust framework where no user or system, internal or external, is automatically trusted.
- Apply strict identity verification and authorization protocols for all access requests, including those from third-party vendors.
Promote Employee Cybersecurity Awarness
- Provide ongoing cybersecurity training to educate staff about phishing, social engineering, and safe online practices.
- Conduct simulated phishing attacks and routine cyber drills to improve preparedness and response capabilities.
Conclusion
As industrial sectors undergo rapid digital transformation, the need for robust cybersecurity measures has never been more critical. With increasing connectivity, industrial control systems are becoming high-value targets for hackers, nation-state actors, and insider threats. A single breach can disrupt essential services, endanger lives, and compromise national security. Therefore, investing in comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks—encompassing threat detection, access control, network protection, and employee awareness—is not just a protective measure but a strategic imperative. As threats continue to evolve, organizations must adopt a proactive, resilient, and AI-driven approach to secure their industrial operations and ensure uninterrupted service delivery in an increasingly connected world.
As a CERT-In empanelled organization, Kratikal is equipped to enhance your understanding of potential risks. Our manual Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) services proficiently discover, detect, and assess vulnerabilities within your IT infrastructure. Additionally, Kratikal provides comprehensive security auditing services to ensure compliance with various regulations, including ISO/IEC 27001, GDPR, PCI DSS, and more, assisting your business in adhering to legal requirements set forth by diverse governments.
FAQs
- What is industrial cybersecurity?
Industrial cybersecurity involves safeguarding critical infrastructure, such as manufacturing facilities, power grids, chemical plants, and other industrial control systems (ICS), against cyberattacks.
- What is a mode of operation in cybersecurity?
A mode of operation defines the method for repeatedly using a cipher’s single-block function to securely encrypt data that exceeds the size of one block. Typically, each encryption process requires a unique binary sequence known as an initialization vector (IV).
The post Essential Cybersecurity Measures to Secure Industrial Operations appeared first on Kratikal Blogs – Information Hub For Cyber Security Experts.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Kratikal Blogs – Information Hub For Cyber Security Experts authored by Shikha Dhingra. Read the original post at: https://kratikal.com/blog/essential-cybersecurity-measures-to-secure-industrial-operations/



