Implementing Exposure Management in Legacy Enterprise Environments
The successful implementation of CTEM for Exposure Management in Legacy Enterprise Environments in legacy systems is crucial, as these systems are the hidden backbone of many large enterprises, comprising more than 30% of business-critical applications in Fortune 500 companies (Gartner, 2023).
These systems, often running on outdated or unsupported operating environments, are involved in essential financial, manufacturing, and communication processes. However, they pose complex cybersecurity risks due to their lack of telemetry, inflexible architectures, and inability to integrate with modern defense-in-depth frameworks.
In fact, recent research by Ponemon Institute indicates that 54% of data breaches are linked to vulnerabilities in legacy systems (Ponemon Report, 2023). Moreover, 62% of security leaders admit they have minimal visibility into the exposure levels of these systems (CSO Online, 2023).
Traditional security strategies have failed to keep up with the dynamic nature of modern threat landscapes, particularly regarding aging infrastructure. Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM), a concept advanced by Gartner, provides a strategic framework to identify, validate, prioritize, and mobilize responses to cyber risks on an ongoing basis. This blog provides a technically grounded roadmap for embedding CTEM into legacy-heavy enterprises, aligning both organizational priorities and operational execution.
The Business Imperative for CTEM in Legacy Environments
Legacy systems are not merely outdated, they are often:
- Mission-critical and high-risk
- Poorly documented
- Out of vendor support
- Incompatible with modern security tools
- Difficult to patch without downtime
- Linked to shadow dependencies
- Non-compliant with modern regulations
- Invisible to security monitoring tools
These systems create persistent exposure windows that adversaries exploit—sometimes silently for months.
A CTEM approach transforms this challenge by enabling organizations to:
- Continuously identify exposed assets
- Validate which exposures are exploitable
- Prioritize based on business impact
- Mobilize timely, coordinated remediation
CTEM isn’t about securing everything; it’s about securing what truly matters.
In a legacy-heavy enterprise, this shift is not optional; it’s foundational to resilience. A CTEM approach shifts organizations from reactive to proactive risk management, ensuring continuous visibility, prioritization, and response.
Key Drivers for CTEM Adoption
- Increased regulatory scrutiny
- Expansion of hybrid cloud infrastructures
- Sophistication of threat actors
- Board-level demand for real-time risk visibility
Also Read: The Evolving Landscape of Security: From Vulnerability Management to CTEM
Organizational Roadmap for CTEM Implementation
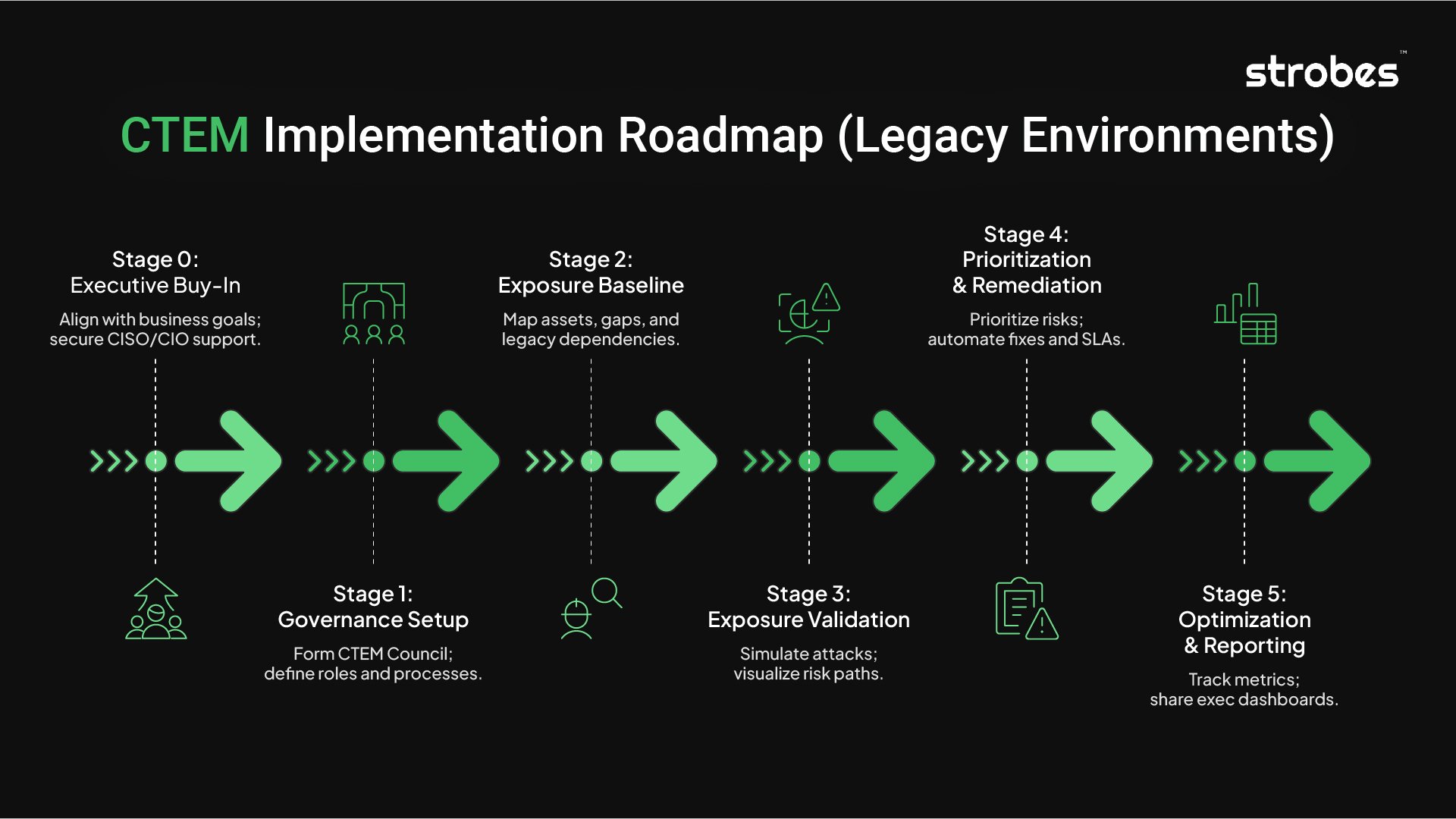
The successful implementation of CTEM for Exposure Management in Legacy Enterprise Environments depends on a structured, multi-stage approach that combines strategic governance with operational readiness. Below is a refined roadmap designed to help large enterprises align CTEM initiatives with core business objectives, risk management practices, and cross-functional accountability.
Stage 0: Executive Buy-In and Strategic Mandate
Objective: Position CTEM as a critical enterprise-wide initiative that supports resilience, risk management, and regulatory alignment.
Key Actions:
- Present data-driven justification for CTEM: cost of unmanaged exposure, breach likelihood, and regulatory impact.
- Align CTEM with broader digital transformation, cloud migration, and IT modernization strategies.
- Secure formal sponsorship from CISO, CIO, and CRO.
- Define funding models and internal success metrics tied to business risk reduction.
- Establish executive CTEM oversight via board-level risk committees.
Stage 1: Governance and Cross-Functional Ownership
Objective: Build a scalable governance structure that supports policy enforcement, operational execution, and strategic accountability.
Key Actions:
- Establish a CTEM Governance Council with leadership from Security, Infrastructure, Risk, Compliance, DevOps, and Line of Business (LoB) owners.
- Define roles and responsibilities across the CTEM lifecycle (discovery, validation, remediation, reporting).
- Integrate CTEM responsibilities into existing ITSM, IR, and asset management teams.
- Launch a CTEM operations charter outlining scope, risk tolerance levels, and escalation procedures.
- Mandate regular governance reviews (monthly tactical, quarterly strategic).
Stage 2: Exposure Baseline Mapping
Objective: Establish foundational visibility into the enterprise asset landscape, including undocumented legacy infrastructure.
Key Actions:
- Consolidate all asset inventories (on-prem, cloud, OT, IT) into a single source of truth.
- Identify visibility gaps such as unmanaged, orphaned, or unsupported legacy systems.
- Evaluate coverage of scanners, endpoint agents, and monitoring systems across environments.
- Initiate workshops with IT and business units to validate asset ownership and criticality.
- Map dependencies between applications, services, and legacy components to understand operational impact.
Deliverables:
- Unified Asset Visibility Report
- CMDB/Inventory Gap Analysis
- Legacy Dependency Matrix
- System Visibility Scorecard
Stage 3: Exposure Validation and Risk Quantification
Objective: Translate raw vulnerabilities and exposures into validated, business-contextualized risk insights.
Key Actions:
- Run attack path modeling and breach simulation exercises across critical legacy systems.
- Validate exploitability of high-severity findings using red teaming or manual testing.
- Correlate findings with threat intelligence (EPSS, CVE trends, exploit kits) to assess real-world risk.
- Tag vulnerabilities based on business impact, exposure level, and downstream dependencies.
- Quantify exposure via scoring models and risk heatmaps to inform prioritization.
Deliverables:
- Exposure Risk Heatmap
- Validated Exploitability Report
- Attack Path Maps for High-Impact Legacy Workloads
- Initial CTEM Risk Baseline Report
Output: Exposure Baseline Report with visibility gaps, remediation SLAs, and asset criticality tiers.
Stage 4: Prioritization and Response Orchestration
Objective: Translate validated exposures into prioritized, actionable remediation workflows.
Key Actions:
- Design a contextual risk scoring model using CVSS, EPSS, asset value, and business impact.
- Tag exposures with urgency levels and map them to SLA-bound remediation protocols.
- Automate ticketing into ITSM tools (e.g., Jira, ServiceNow) with ownership routing.
- Enable re-validation loops post-patching and risk closure.
- Align remediation timelines with infrastructure, DevOps, and LoB performance KPIs.
Deliverables:
- Prioritized Vulnerability Queue
- Remediation Playbooks by Risk Tier
- SLA Tracker with Escalation Matrix
- Cross-Team Ownership Map
Stage 5: Continuous Optimization and Executive Reporting
Objective: Institutionalize exposure reduction through feedback loops, dashboards, and executive insights.
Key Actions:
- Monitor MTTR, SLA compliance, and recurrence across business units.
- Feed metrics into monthly, quarterly, and bi-annual CTEM governance cycles.
- Publish executive dashboards with heatmaps, trends, and compliance views.
- Calibrate CTEM processes based on audit findings, red team outputs, and business shifts.
- Align CTEM reporting with enterprise GRC and board-level risk narratives.
Deliverables:
- Executive CTEM Dashboard
- Risk Elimination Trend Reports
- GRC & Audit-Aligned Reports
- Quarterly CTEM Improvement Plan
Designing the CTEM Lifecycle for Legacy Systems
The CTEM lifecycle consists of five operational pillars:
Enterprise Integration & Cultural Shift
To successfully operationalize CTEM, organizations must embed it into the workflows and systems already in use, while fostering a mindset shift across teams. This requires tight integration with core business systems and deliberate efforts to promote cultural adoption.
Seamless Enterprise Integration
- Embed CTEM Findings into ITSM Pipelines: Route validated exposures into ticketing systems like ServiceNow or Jira with pre-set remediation SLAs.
- Align with GRC and Compliance Systems: Feed exposure metrics into risk registers and audit dashboards to reinforce accountability.
- Bridge to DevSecOps: Integrate CTEM outputs into CI/CD workflows to flag high-risk vulnerabilities before release.
- Establish Cross-System Data Flows: Synchronize asset intelligence and threat context across EDR, CMDB, and SIEM platforms.
- Tie Remediation to Performance Management: Make risk closure timelines a formal KPI for infrastructure and application owners.
Driving Cultural Normalization
- Institutionalize CTEM in Incident Response Drills: Treat exposure insights as core components of IR exercises and tabletop scenarios.
- Gamify Risk Reduction: Introduce leaderboards or incentives for teams that demonstrate the highest closure rate on critical exposures.
- Make Exposure Metrics Visible: Publish CTEM dashboards to executive stakeholders, showcasing trends, bottlenecks, and wins.
- Create Champions: Identify CTEM ambassadors across business units to evangelize best practices and improve adoption.
- Celebrate Remediation Milestones: Publicly recognize departments or teams that significantly improve their risk posture.
With integration and culture in sync, CTEM transitions from a technical program into a living, breathing part of enterprise resilience.
- Run CTEM simulations during incident response exercises
- Reward business units for reducing risk exposure
- Communicate CTEM successes in executive dashboards
Metrics and Operational Feedback Loops
Establishing a mature CTEM program requires actionable, business-relevant metrics that inform continuous improvement across security, IT, and leadership teams. These metrics must go beyond raw counts to offer meaningful insight into risk reduction and remediation efficiency.
Core CTEM Metrics Framework
CTEM Operational Metrics
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Asset Visibility Coverage | % of assets with full visibility across IT, OT, cloud, and legacy systems. |
| Validated Risk Density | Volume of exploitable vulnerabilities per 1,000 assets. |
| Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR) | Average duration from exposure detection to resolution. |
| SLA Compliance Rate | Percentage of issues resolved within defined remediation timelines. |
| Attack Path Elimination | Number of lateral movement paths neutralized through configuration changes. |
| Recurring Vulnerability Index | Frequency and volume of vulnerabilities that reappear after remediation. |
| CTEM Coverage Score | Weighted score reflecting CTEM process maturity and control reach. |
| Exposure to Exploitation Gap | Average time between detection and validation of actively exploitable risks. |
Reporting & Feedback Cadence
| Frequency | Stakeholder Focus | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|
| Weekly | SOC, Infra, AppSec Teams | Tactical remediation metrics, exposure alerts |
| Monthly | CTEM Council, Security Ops | Exposure trends, SLA adherence, key blockers |
| Quarterly | Business Unit Heads, Risk Committees | Risk posture summaries, asset-level exposure heatmaps |
| Bi-Annually | Board, Executive Leadership | Strategic CTEM impact report, investment proposals |
By embedding these metrics into dashboards and strategic reviews, CTEM becomes an integral part of how the enterprise quantifies, communicates, and accelerates security outcomes.
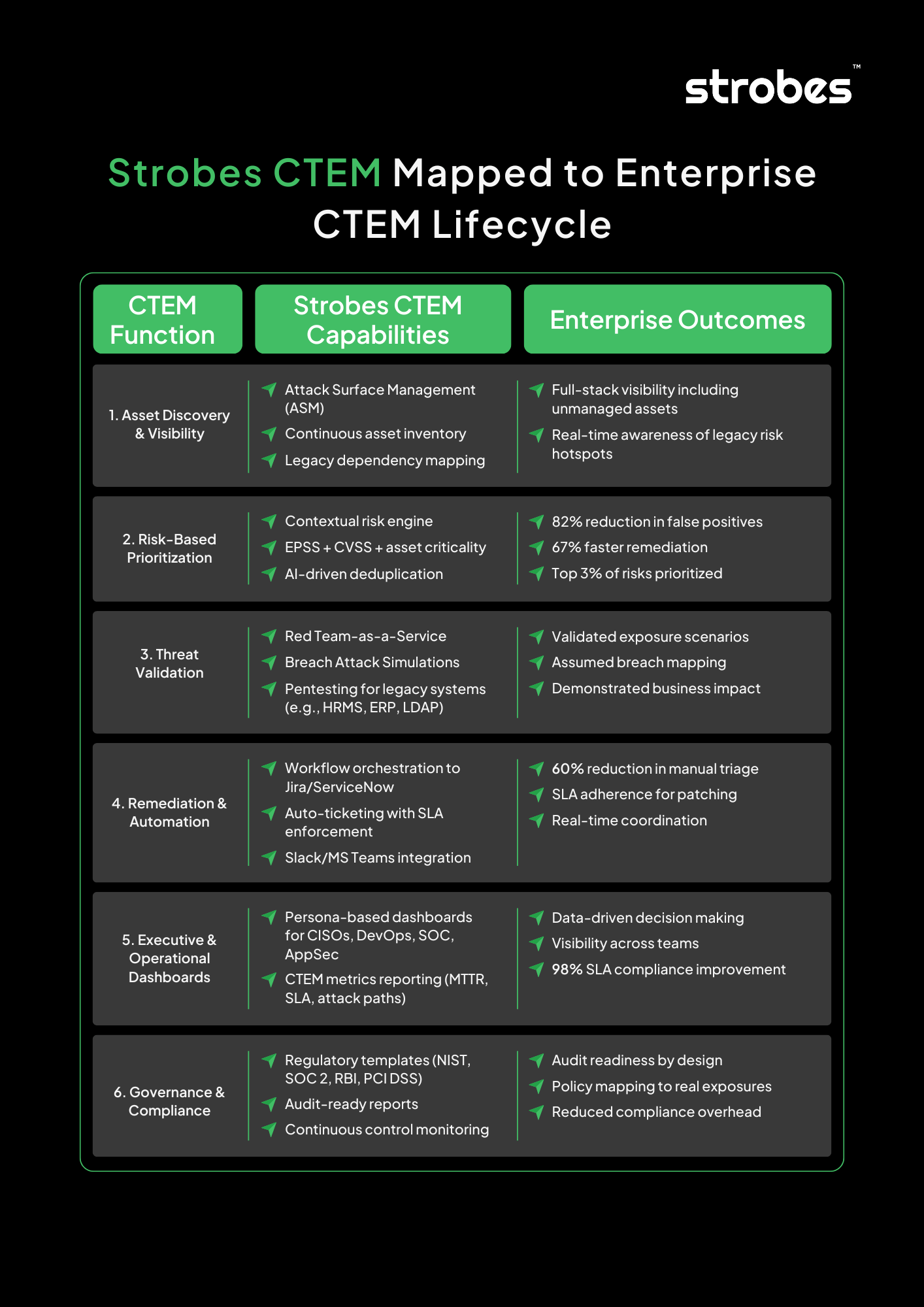
Strobes CTEM Mapped to Enterprise CTEM Lifecycle
Legacy systems will not disappear overnight. But neither should your exposure remain unmanaged. By institutionalizing CTEM as a strategic function—and not just a security project—you evolve from managing vulnerabilities to managing risk in motion.
The real transformation happens not in tool deployment, but in how your people, processes, and priorities align to defend against tomorrow’s threats, starting today.
Strobes CTEM (Continuous Threat Exposure Management) platform is purpose-built to help enterprises overcome the complexity of legacy systems while implementing a modern, scalable exposure management program. Its modular architecture spans the full CTEM lifecycle—from asset discovery and prioritization to threat validation, automated remediation, and executive reporting. Below is a consolidated view of how Strobes aligns with each functional pillar of an enterprise CTEM program, especially within hybrid and legacy-heavy environments.
Why Strobes CTEM is Enterprise-Ready for Exposure Management in Legacy Enterprise Environments:
For CISOs and CIOs, the challenge isn’t just identifying vulnerabilities in legacy systems—it’s making sense of them in a business context, prioritizing what matters, and operationalizing a response without disrupting critical workflows. That’s precisely where Strobes CTEM adds unique enterprise value.
| Attribute | Enterprise Benefit |
|---|---|
| Modular Stack (ASM + PTaaS + RBVM + ASPM) | Full CTEM lifecycle coverage with deep legacy integration |
| AI-powered deduplication | Shrinks noise from redundant legacy scan outputs |
| 120+ integrations | Connects with legacy CMDBs, SIEMs, scanners, and ITSM platforms |
| Compliance-Ready Framework | Aligns with NIST, PCI-DSS, OWASP, RBI, SOC2 and other frameworks |
| Developer-first remediation | Secure SDLC workflows with actionable insights, not generic patch guidance |
1. It adapts to your architecture, not the other way around.
Legacy environments are often rigid, undocumented, and fragile. Strobes doesn’t force change—it works with your existing tools, networks, and operational constraints, layering intelligence and orchestration on top.
2. CTEM becomes part of IT and business decision-making—not just a security dashboard.
Strobes don’t stop at security. It feeds exposure intelligence into change management, DevOps, GRC, and procurement, making CTEM an input into enterprise-wide planning—not a siloed function.
3. It empowers risk ownership beyond the security team.
With persona-based dashboards and workflow assignment, Strobes enables application owners, IT ops, and business leaders to take ownership of remediation within their lanes—bridging the cultural divide between detection and action.
4. Built-in defensibility for audits and regulators.
For systems that can’t be patched, Strobes helps CISOs defend their position with validated compensating controls, attack path isolation, and contextual risk scoring—essential during compliance audits and board reviews.
5. It’s designed to scale with your transformation journey.
Whether you’re in the early stages of infrastructure modernization or managing a multi-cloud estate with embedded legacy systems, Strobes grows with you—helping you reduce exposure without waiting for a tech overhaul.
Conclusion: From Legacy Risk to Strategic Resilience
Legacy systems are not going away anytime soon, but that doesn’t mean they have to remain unmanaged security liabilities. With the right strategy, visibility, and orchestration, organizations can turn these high-risk assets into actively governed components of their cyber defense strategy.
Exposure Management in Legacy Enterprise Environments, powered by Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM), offers the enterprise-grade framework needed to evolve from fragmented vulnerability handling to a continuous, contextual, and proactive exposure reduction model. When applied thoughtfully across legacy-heavy environments, CTEM bridges the gap between operational continuity and modern risk management.
By following a phased implementation roadmap and leveraging platforms like Strobes CTEM, security and IT leaders can embed exposure management into every layer of the enterprise—without disrupting business-critical operations.
Legacy doesn’t have to mean vulnerable. With CTEM, it can mean informed, intentional, and under control.
Schedule Your Free Consultation.
Related Reads:
- CTEM for SaaS Security Leaders: A Practical Guide
- Key CTEM Metrics: Measuring the Effectiveness of Your Continuous Threat Exposure Management Program
- The Evolving Landscape of Security: From Vulnerability Management to CTEM
- How CTEM Impacts Cyber Security Insurance Premiums?
- How CTEM Enhances Threat Prioritization in Complex Networks
- Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) – The Ultimate Guide for CISOs
- Solution: One Platform For All The Offensive Security Needs
The post Implementing Exposure Management in Legacy Enterprise Environments appeared first on Strobes Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Strobes Security authored by strobes. Read the original post at: https://strobes.co/blog/exposure-management-in-legacy-enterprise-environments/



