Understanding Advanced Persistent Threats
What are Advanced Persistent Threats(APTs)?
Advanced persistent threats (APTs) are a type of cyber attack that poses a serious threat to organizations and individuals alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of APTs, exploring what they are, how they work, and the impact they can have. So, let’s begin by understanding what exactly an advanced persistent threat is.
Understanding Advanced Persistent Threats:
Definition and Overview:
At its core, an advanced persistent threat refers to a stealthy, targeted attack that is carried out by skilled and well-funded adversaries. Unlike more common cyber attacks that are short-lived and opportunistic, APTs are known for their persistence, often infiltrating an organization’s network and remaining undetected for extended periods of time. This allows the attackers to gain a foothold and carry out their malicious activities without raising alarm bells.
According to allied market research, the global advanced persistent threat market was valued at $5.9 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $30.9 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 20.5% from 2022 to 2030.

Key Findings of Advanced Persistent Threats:
According to the Kaspersky Q3 2023 report, the most significant key findings among APT groups are:
- APAC Government Attack via USB: In this quarter, government entities in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region were targeted by compromising secure USB drives.
- Non-Technical APT Success: The BlindEagle APT group’s activities in Latin America highlight that not all successful APT incidents require high technical sophistication.
- Toolset Advancements: Established threat actors are continuously enhancing their toolsets. Notable examples include ScarCruft’s multi-stage infection chain, successive RATs used by BlindEagle, and MuddyWater’s VPN application emulation.
- The Emergence of BadRory: A new threat actor, BadRory, has surfaced and conducted campaigns.
- Global APT Campaigns: APT campaigns remain geographically dispersed, with actors targeting Europe, South America, the Middle East, and various parts of Asia.
- Diverse Target Sectors: APT attacks have impacted a wide range of sectors, including government, military, defense, gaming, software, entertainment, utilities, finance, and manufacturing.
- Geo-Political Influence: Geo-political factors continue to drive APT development, with cyber espionage remaining a primary goal of these campaigns.
Stages of an Advanced Persistent Threat (APT):
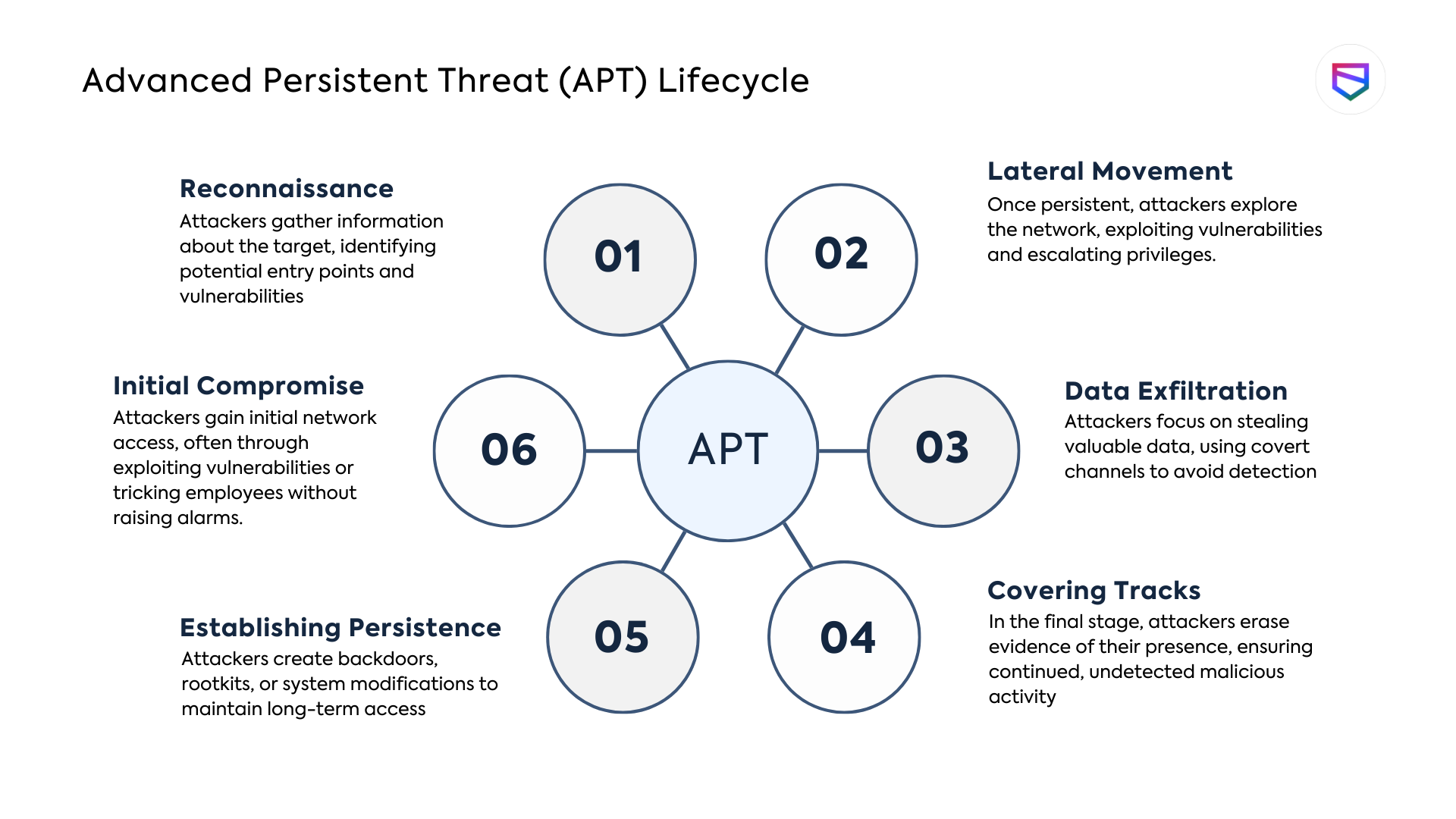 By understanding the various stages of an APT attack, organizations can better prepare themselves to detect, prevent, and respond to these sophisticated threats.
By understanding the various stages of an APT attack, organizations can better prepare themselves to detect, prevent, and respond to these sophisticated threats.
Implementing robust security measures, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and educating employees about the risks of social engineering are some of the strategies organizations can adopt to mitigate the risk of falling victim to an APT.
Mitigations of Advanced Persistent Threat:
- Implementing Robust Security Measures:
- Deploy advanced security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, and endpoint protection, to detect and prevent APT attacks.
- Utilize access controls, multi-factor authentication, and network segmentation to limit attack surfaces and control access.
- Conducting Regular Vulnerability Assessments:
- Periodically assess the organization’s systems and network for vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Address identified vulnerabilities promptly by applying security patches and updates.
- Educating Employees about Social Engineering Risks:
- Provide regular training on APT awareness, emphasizing the risks associated with social engineering attacks like phishing and pretexting.
- Encourage employees to be vigilant and report suspicious activities promptly.
- Implementing Incident Response Plans:
- Develop comprehensive incident response plans to respond effectively when an APT attack is detected.
- Practice and update these plans to ensure they are current and efficient.
- Engaging Threat Intelligence:
- Subscribe to threat intelligence services to stay informed about APT groups, their tactics, and indicators of compromise.
- Use this intelligence to proactively bolster security measures.
By adopting these strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their resilience against APT attacks.
Impact of Advanced Persistent Threats:
- Financial Consequences: APTs result in costly investigations, data breach expenses, lawsuits, fines, and loss of revenue.
- Operational Disruptions: APTs cause network outages, data loss, and compromised systems, disrupting day-to-day operations.
- Reputational Damage: APTs harm an organization’s reputation, leading to lost trust, customer loyalty, and business opportunities.
Conclusion:
Advanced persistent threats are highly sophisticated and targeted cyber attacks that can have far-reaching consequences for organizations and individuals. Understanding the nature of APTs, their anatomy, types, and impact is crucial in developing effective strategies to detect, prevent, and respond to these evolving threats. By staying informed and implementing robust security measures, organizations can better defend against APTs and minimize the potential harm they can inflict.
Recommended Reading:
Top 7 Most Trusted Cybersecurity Firms in India
Endpoint Security: The Least Privilege Approach
Behind the Screens: Exposing the Diverse Range of Daily Cyber Attacks
The post Understanding Advanced Persistent Threats appeared first on WeSecureApp :: Simplifying Enterprise Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from WeSecureApp :: Simplifying Enterprise Security authored by Naimisha. Read the original post at: https://wesecureapp.com/blog/understanding-advanced-persistent-threats/



