Unlocking Endpoint Encryption: What’s New in 2023?
Introduction
In the digital age of 2023, the world is more connected than ever before. With the rise of cloud computing, remote work, and online transactions, data has become the lifeblood of businesses, especially for small enterprises. But with this increased connectivity comes an elevated risk. Cyber threats, data breaches, and hacking attempts are no longer confined to large corporations; small businesses are equally, if not more, vulnerable. This is where endpoint encryption steps in as a guardian.
For small businesses, every piece of data, be it customer information, financial records, or internal communications, holds immense value. A single breach can not only lead to financial losses but can also tarnish the reputation they’ve painstakingly built over the years. Endpoint encryption acts as a formidable barrier, ensuring that even if data falls into the wrong hands, it remains an indecipherable jumble of characters, useless to prying eyes. In essence, it’s not just a technical jargon but a crucial shield in today’s perilous digital landscape, safeguarding a business’s most precious asset: its data.
What is Endpoint Encryption?
At its core, encryption is the process of converting readable data, known as plaintext, into an unreadable format, called ciphertext, using a specific algorithm. This transformation ensures that even if someone intercepts the data, they won’t be able to understand it without the appropriate decryption key. Think of it as converting a clear message into a secret code that only someone with a special key can decipher.
Endpoint encryption takes this concept and applies it specifically to ‘endpoints’ in a network. An endpoint can be any device that communicates back and forth with a network, such as computers, smartphones, or tablets. Given the myriad of threats these devices face, from malware to physical theft, encrypting the data they hold becomes paramount.
But how does endpoint encryption differ from regular encryption? While the foundational principle remains the same, endpoint encryption focuses on securing data at rest on individual devices. Regular encryption might encompass a broader range of applications, including data in transit over the internet or within network systems. Endpoint encryption ensures that the data stored on a device remains secure, even if the device itself is compromised.
In today’s world, where we’re constantly connected and data flows seamlessly across devices, ensuring the security of each endpoint becomes a cornerstone of a robust cybersecurity strategy. Whether it’s a confidential business document on a laptop or customer data on a server, endpoint encryption ensures it’s shielded from prying eyes.
Why Endpoint Encryption Matters in 2023
As we navigate through 2023, the digital realm continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace. With this evolution, however, comes a darker side: the escalating landscape of cyber threats. Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated, leveraging advanced techniques to exploit vulnerabilities and breach systems. Small businesses, often perceived as ‘easier targets’ due to limited cybersecurity resources, find themselves at the forefront of these attacks.
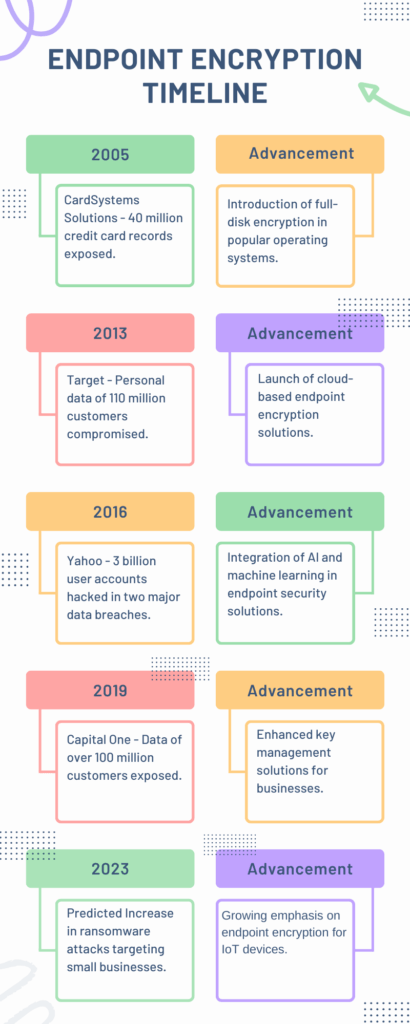
The infographic below paints a vivid picture of the major data breaches over the years. From the CardSystems Solutions breach in 2005, affecting 40 million credit card records, to the colossal Yahoo breach in 2016, compromising 3 billion user accounts, the scale and impact of these incidents are staggering. And as we delve deeper into 2023, predictions indicate a surge in ransomware attacks specifically targeting small businesses.
But amidst this grim landscape, there’s a beacon of hope: encryption. Let’s consider the Equifax breach of 2017. Personal information of 147 million people was exposed, but imagine if that data had been encrypted. The hackers would have been left with indecipherable gibberish, rendering the stolen data useless. Similarly, the Capital One breach in 2019, which exposed data of over 100 million customers, could have had a different outcome with robust endpoint encryption in place.
Endpoint encryption acts as the last line of defense. Even if cybercriminals manage to bypass other security measures, encrypted data remains a fortress, impenetrable without the decryption key. In a world where data breaches are not a matter of ‘if’ but ‘when’, endpoint encryption stands as a vital shield, safeguarding businesses from the catastrophic consequences of data exposure.
As we move forward in 2023, with an ever-evolving cyber threat landscape, the role of endpoint encryption becomes not just important, but indispensable. For small businesses aiming to thrive in this digital age, it’s a security measure that simply cannot be overlooked.
Types of Endpoint Encryption
When it comes to securing data at the endpoint level, there are two types of encryption methods that businesses can employ: Whole Drive Encryption and File, Folder & Removable Media Encryption. Each method has its unique advantages and potential drawbacks, depending on the specific needs and infrastructure of a business.
Whole Drive Encryption
Whole drive encryption is a method that encrypts the entire hard drive of a device. Everything, including the operating system, system files, and user files, is encrypted. It offers a blanket layer of security, ensuring that all data on the drive is encrypted and protected from unauthorized access. Once set up, users don’t have to decide what to encrypt. Everything is automatically encrypted.
However, encrypting the entire drive can sometimes lead to a slight decrease in system performance, especially during the initial encryption process. Also, if the encryption key is lost or if there’s a system failure, recovering data can be challenging.
File, Folder & Removable Media Encryption
This method of encryption allows users to selectively encrypt specific files, folders, or removable media like USB drives. With this method, users can choose which data to encrypt, allowing for a balance between security and accessibility. It’s particularly useful for businesses that frequently use removable media. Encrypting specific files ensures that data remains secure even if the media is lost or stolen.
However, if users forget to encrypt sensitive files, those files remain vulnerable. It also requires more active management to ensure that all critical data is encrypted.
In today’s digital age, where data breaches are becoming increasingly common, employing endpoint encryption is not just a best practice but a necessity. Whether a business opts for whole drive encryption for its comprehensiveness or file and folder encryption for its flexibility, the key is to ensure that sensitive data remains inaccessible to unauthorized users. As cyber threats continue to evolve, staying informed and proactive in data protection strategies is paramount for businesses of all sizes.
How Encryption Protects Stolen Data
In the realm of cybersecurity, a common misconception is that encryption is solely about keeping unauthorized individuals from accessing data. While this is a primary function, encryption’s true power lies in its ability to render stolen data useless. Let’s delve into how this works.
The Magic of Encryption
Imagine you’ve written a secret message on a piece of paper. If someone were to steal that paper, they’d easily read your message. Now, consider if you had written that message in a code only you understood. The thief might have the paper, but the message remains a mystery. This is the essence of encryption.
When data is encrypted, it’s transformed into a complex code. This code, or “cipher text,” is indecipherable without the correct decryption key. So, even if a cybercriminal manages to steal encrypted data, they’re left with a jumbled mess of characters. Without the decryption key, this data is as good as gibberish.
The Role of Encryption Keys
Encryption keys are the heart of data security when it comes to encryption. Think of them as the unique codebook to your secret message. There are two primary types of encryption keys. Symmetric key uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. It’s like having a single key that both locks and unlocks a door. While simpler, it poses a risk. If the key is lost or stolen, the data is compromised. Asymmetric keys involves a pair of keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. Imagine a mailbox where anyone can drop in a letter (public key), but only the owner can open and read the letters with a special key (private key).
The security of encrypted data is intrinsically tied to the security of its encryption keys. If keys are mishandled, lost, or stolen, the encrypted data is at risk. Therefore, robust key management practices are essential. This involves securely generating, distributing, storing, and periodically rotating keys.
In conclusion, while encryption acts as a formidable barrier against unauthorized access, its true strength lies in its ability to protect data even when it falls into the wrong hands. It can render stolen data unreadable and ensuring robust key management. Thus, businesses can significantly bolster their defense against cyber threats.
Securing Data Transfers with Encryption
In today’s interconnected world, data is constantly on the move. Whether it’s a business sending sensitive information to a partner, a consumer making an online purchase, or an employee accessing company files remotely, data transfers are ubiquitous. However, every time data is transmitted over the internet, it’s vulnerable to interception. This is where the importance of encrypting data during transfers comes into play.
The above diagram showcases the journey of data from a sender’s device to a receiver’s device. In the absence of encryption, data can be easily intercepted, making it vulnerable to unauthorized access. However, when encryption is employed, the data travels securely, ensuring its protection even if someone tries to intercept it.
Why Encrypt Data During Transfers?
- Confidentiality: Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted during transmission, it remains confidential. Only the intended recipient, possessing the correct decryption key, can access the original data.
- Integrity: Encryption also ensures the integrity of the data. Any tampering during transmission can be detected, ensuring that the data received is exactly as it was sent.
- Authentication: Through encryption, both the sender and receiver can verify each other’s identities, ensuring that the data is being sent to and received from the intended parties.
- Non-repudiation: Once data is sent, the sender cannot deny having sent it, and the receiver cannot deny having received it. This is crucial for transactions where proof of communication is essential.
In conclusion, as cyber threats continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, the need for secure data transfers has never been more paramount. By encrypting data during transmission, businesses and individuals can ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of their data. Thus, safeguarding it from potential cyber threats.
Key Management in Endpoint Encryption
Endpoint encryption is a powerful tool in the cybersecurity arsenal, but its effectiveness hinges on one crucial aspect: key management. At its core, key management revolves around the creation, storage, distribution, and retirement of encryption keys. These keys, which are used to encrypt and decrypt data, are the linchpin of any encryption strategy. If they fall into the wrong hands, the very data they’re meant to protect becomes vulnerable. Thus, understanding and implementing robust key management practices is paramount.
Introduction to Key Management
Key management is the administrative process of handling and maintaining cryptographic keys used in the encryption and decryption process. These keys, akin to digital passwords. They are essential for ensuring the security of encrypted data. Without proper key management, even the most sophisticated encryption algorithm can be rendered ineffective.
Significance of Key Management
- Data Security: The primary purpose of encryption is to protect data. However, if encryption keys are mishandled or compromised, the encrypted data is at risk. Proper key management ensures that keys are securely generated, stored, and retired, safeguarding the data they protect.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries have regulations that mandate the secure handling of data. Proper key management practices can help businesses comply with these regulations, avoiding potential legal and financial repercussions.
- Operational Continuity: Losing access to encryption keys can result in the loss of critical data. Effective key management ensures that businesses can always access their encrypted data, ensuring operational continuity.
Storing and Managing Encryption Keys
- Keystore: A keystore is a secure repository used to store encryption keys. It provides a centralized location for key storage, ensuring that keys are readily available when needed and protected from unauthorized access.
- Key Rotation: Regularly changing encryption keys enhances security. Old keys are retired, and new ones are generated, ensuring that even if a key is compromised, it won’t be useful for long.
- Key Backup: It’s essential to have backup copies of encryption keys. This ensures that if a key is lost or corrupted, there’s a backup available, preventing potential data loss.
- Access Control: Not everyone in an organization should have access to encryption keys. Implementing strict access controls ensures that only authorized personnel can access and manage keys.
- Key Lifecycle Management: From the moment an encryption key is generated to the moment it’s retired, it goes through various stages. Managing this lifecycle, including key generation, distribution, rotation, and retirement, is crucial for maintaining data security.
In conclusion, while endpoint encryption is a powerful tool for data protection, its effectiveness is closely tied to robust key management practices. By understanding and implementing these practices, businesses can ensure the security and integrity of their encrypted data.
Glossary of Encryption Terms
Encryption, while a powerful tool for data protection, comes with its own set of jargon that can be daunting for those unfamiliar with the subject. To make the topic more approachable and to ensure clarity, we’ve compiled a glossary of key encryption terms. This glossary serves as a quick reference guide, helping readers understand the fundamental concepts associated with encryption.
Refer to the infographic for a visual representation of the key terms associated with encryption.
Key Terms:
- Encryption: The process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access.
- Decryption: The process of converting encrypted data back to its original form.
- Cipher: An algorithm used for performing encryption or decryption.
- Public Key: A cryptographic key that can be publicly shared and is used to encrypt data.
- Private Key: A secret cryptographic key used for decryption. Paired with a public key in asymmetric encryption.
- Symmetric Encryption: Encryption where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption.
- Asymmetric Encryption: Encryption where different keys (public and private) are used for encryption and decryption respectively.
- Key Rotation: The practice of periodically changing encryption keys to enhance security.
Understanding these terms is crucial for anyone looking to delve deeper into the world of encryption and cybersecurity. Whether you’re a small business manager or an IT professional, having a grasp of these fundamental concepts will empower you to make informed decisions regarding data protection and security.

Choosing the Right Endpoint Encryption Solution
In today’s digital age, where cyber threats are ever-evolving, selecting the right endpoint encryption solution is paramount for any business, especially small businesses. With a myriad of options available, making the right choice can be overwhelming. Here, we break down the key factors to consider when selecting an endpoint encryption solution and provide an overview of some of the popular solutions in 2023.
Factors to Consider:
- Ease of Use: The solution should be user-friendly, ensuring that even those with limited technical expertise can navigate and utilize its features effectively.
- Scalability: As your business grows, your encryption needs may evolve. Choose a solution that can scale with your business, accommodating more devices and data as needed.
- Key Management: Effective key management is crucial for any encryption solution. Ensure the solution offers robust key management features, including key generation, storage, rotation, and backup.
- Compatibility: The solution should be compatible with the devices and platforms your business uses. Whether it’s Windows, macOS, Linux, or mobile devices, ensure the solution supports them.
- Support and Updates: Cyber threats are constantly evolving. Choose a solution that offers regular updates to counter new threats and provides prompt customer support when needed.
Popular Endpoint Encryption Solutions in 2023:
- ESET Endpoint Encryption: Known for its comprehensive encryption capabilities, ESET offers full disk encryption, file and folder encryption, and email encryption. It’s user-friendly and offers robust key management features.
- Symantec Endpoint Encryption: A trusted name in the cybersecurity world, Symantec provides powerful encryption for both full disks and removable media. It also boasts advanced threat protection features.
- Armour Zero Secure: Tailored for businesses looking for a holistic security solution, Armour Zero Secure offers endpoint encryption combined with threat detection and response capabilities.
- BitLocker: Integrated into Windows operating systems, BitLocker offers full disk encryption for Windows devices. It’s straightforward to set up and is ideal for businesses primarily using Windows.
- McAfee Total Protection: Beyond just endpoint encryption, McAfee offers a suite of security features, including malware protection, firewall, and web security. Its encryption features are robust and suitable for diverse business needs.
In conclusion, choosing the right endpoint encryption solution requires a careful evaluation of your business’s specific needs and the features offered by different solutions. By considering the factors listed above and exploring the popular solutions, you can ensure that your business’s data remains secure and protected against potential cyber threats.
Conclusion: The Future of Endpoint Encryption
In our journey through the realm of endpoint encryption, we’ve delved into its significance, especially for small businesses in today’s digital age. We’ve defined encryption, explored its various types, and highlighted how it acts as a shield, protecting stolen data and ensuring secure data transfers. Through our glossary, we’ve demystified the jargon, making the topic more accessible. And, we’ve provided guidance on choosing the right endpoint encryption solution, emphasizing factors to consider and spotlighting some of the top solutions in 2023.
As we look to the future, it’s evident that the role of endpoint encryption in endpoint security is not static; it’s evolving. With the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats, encryption is becoming more crucial than ever. It’s not just about protecting data at rest but ensuring its safety during transfers, managing encryption keys effectively, and choosing solutions that align with business needs.
For businesses, especially small ones, the message is clear: Endpoint encryption is not a luxury; it’s a necessity. As you chart your endpoint security strategy, prioritize encryption. It’s an investment in safeguarding your business’s most valuable asset: its data. Remember, in the world of cybersecurity, it’s always better to be proactive than reactive. Prioritize, protect, and prosper.
The post Unlocking Endpoint Encryption: What’s New in 2023? appeared first on Endpoint Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Endpoint Security authored by Michael Toback. Read the original post at: https://smallbizepp.com/endpoint-encryption/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=endpoint-encryption



