Botnet Detection in 2023: What You’re Missing Out On!
Introduction
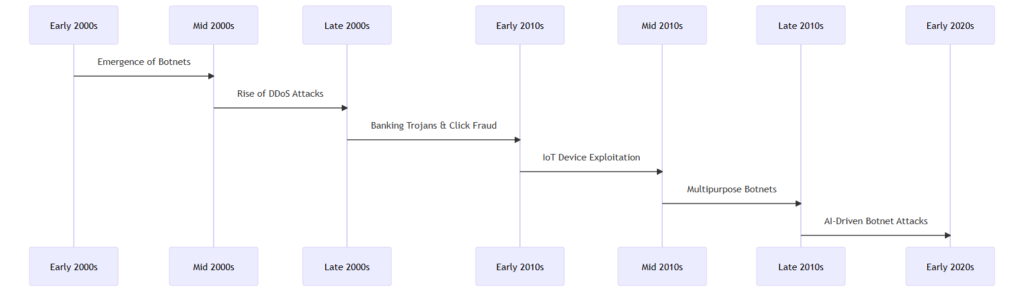
In the realm of cybersecurity, botnet detection has become a paramount concern for businesses worldwide. As we navigate through 2023, the digital landscape continues to evolve, bringing forth both innovations and threats. Among these threats, botnets stand out as one of the most formidable challenges. These networks of compromised devices have been responsible for some of the most devastating cyberattacks in recent history. The rise of botnets is not just a tale of technological advancement gone awry; it’s a testament to the ever-changing nature of cyber warfare. Our visual timeline provides a glimpse into the evolution of botnets, tracing their journey from their inception to their significant role in today’s Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
In our interconnected world, have you ever stopped to ponder the invisible strings that might be tugging at our digital devices? Imagine, for a moment, a puppeteer controlling a vast array of marionettes, each one dancing to a tune unbeknownst to its owner. This, in essence, is the world of botnets—a world that has evolved and expanded right under our noses.
Timeline of Botnets and DDoS Attacks
Back in the early 2000s, if someone had whispered the word ‘botnet’ in a boardroom, they might’ve been met with blank stares. But today, in 2023? It’s a term that resonates with urgency and caution in every IT department and business strategy meeting. Why? Because botnets have become the silent puppeteers of the digital age, manipulating not just isolated computers, but entire networks and even the smart devices we’ve so warmly welcomed into our homes.
Now, let’s embark on a brief journey through time. Picture the digital landscape of the mid-2000s: the internet was booming, and with it came the first ripples of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Fast forward a bit, and the scene was awash with cunning banking trojans and deceptive click frauds. And as the decade turned, our cherished Internet of Things (IoT) devices became the new frontier for these shadowy puppeteers. By the dawn of the 2020s, the game had changed yet again. Botnets, now armed with the power of artificial intelligence, became eerily adept, learning and adapting like a predator in the wild.
So, where does this leave us, the small business managers and the tireless IT teams? In a world of ever-shifting sands, how do we anchor ourselves? The answer lies in knowledge, vigilance, and a collective commitment to safeguarding our digital realm. After all, if we don’t pull the strings, who will?
Understanding Botnets: Detecting More Than Just Malware
What is a botnet?
Have you ever watched a flock of birds move in unison, each individual seamlessly following the collective rhythm? Now, imagine if each bird was a computer, and an unseen force was guiding their synchronized dance. This, in its essence, is the world of botnets.
At its core, a botnet is a network of interconnected devices, each one compromised and controlled by a central entity. But what makes these devices dance to the puppeteer’s tune? It’s a piece of malicious software, often referred to as ‘malware’. But here’s the catch: while all botnets utilize malware, not all malware creates botnets. Confused? Let’s break it down.
Botnet vs Malware
Malware, in its broadest sense, is any software designed to harm or exploit devices. It’s the umbrella term, encompassing everything from viruses to spyware. But botnets? They’re a unique breed. While traditional malware might act as a lone wolf, infiltrating and damaging a single device, botnets operate as a collective. Think of it as the difference between a solitary thief and an organized syndicate. The former might break into a house, but the latter? They can take over an entire neighborhood.
Now, you might be wondering, how do botnets differ from other malware types? The key lies in their collective nature. While a virus might corrupt files on a single computer, a botnet harnesses the power of multiple devices, directing them towards a singular goal. It’s not just about causing chaos; it’s about coordinated, strategic action. And this collective power is what sets botnets apart, making them a formidable force in the cyber realm.
In essence, understanding botnets is akin to understanding the power of unity. Alone, a compromised device might cause limited harm. But together, under the command of a botnet? Their potential is both awe-inspiring and, frankly, a bit terrifying. But fear not, for knowledge is our greatest weapon. And as we delve deeper, we’ll arm ourselves with the insights needed to navigate this intricate web.
The Invisible Threat: How Botnets Operate
The Invisible Threat: How Botnets Operate
In today’s digital landscape, botnets have emerged as one of the most formidable threats. These networks of compromised devices operate silently, often unbeknownst to their owners, carrying out the nefarious agendas of their controllers. Central to the operation of a botnet is its Command & Control (C&C) structure, which orchestrates the activities of the infected devices.
Command & Control (C&C) Structure
The C&C structure is the brain behind a botnet. It’s where the commands originate and where the data from infected devices is sent. There are two primary types of C&C structures:
- Centralized Command & Control: This is the more traditional method where a single server or a small group of servers send commands to and receive data from the bots. While this method offers the bot herder (the individual or group controlling the botnet) a centralized point of control, it also presents a vulnerability. If authorities or cybersecurity experts identify and take down the central server, the entire botnet can be neutralized.
- Peer-to-Peer Command & Control: In this decentralized approach, bots communicate with each other directly, without the need for a central server. Commands can be issued from any bot, and data can be sent to any other bot. This structure is more resilient against takedowns, as there isn’t a single point of failure. However, it’s also more complex to set up and manage.
Role of Infected Devices
Infected devices, often referred to as ‘bots’, are the foot soldiers of a botnet. These can range from personal computers and smartphones to smart fridges and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Once a device is infected, typically through malware, it becomes part of the botnet and can be controlled remotely through the C&C structure.
These bots carry out a variety of tasks, from sending out spam emails and launching Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks to stealing sensitive data. The owners of these devices are usually unaware that their device is part of a botnet, as the malware operates in the background, ensuring the device functions normally to avoid detection.
In conclusion, botnets represent a sophisticated and evolving threat in the cyber landscape. Their ability to harness the power of countless devices, combined with their ever-evolving C&C structures, makes them a significant challenge for cybersecurity professionals. As we continue to connect more devices to the internet, understanding and combating botnets becomes not just a technical necessity but a critical endeavor for the safety of our digital world.
Botnet Detection: The First Line of Defense
In the realm of cybersecurity, the adage “forewarned is forearmed” holds profound significance. Detecting a threat early can mean the difference between a minor inconvenience and a major catastrophe. When it comes to botnets, early detection is paramount. By identifying and addressing a botnet threat in its nascent stages, organizations can prevent extensive damage, protect sensitive data, and maintain their reputation.
The Importance of Early Botnet Detection
- Mitigating Threats: The earlier a botnet is detected, the quicker countermeasures can be deployed. This can prevent the botnet from fully activating, thereby averting potential attacks such as DDoS assaults or data breaches.
- Limiting Spread: Early detection can prevent the botnet from spreading to other devices within a network. This containment can be crucial, especially in large organizations where a single compromised device can lead to a domino effect.
- Financial Implications: The financial repercussions of a successful botnet attack can be staggering. From direct financial losses to the costs associated with damage control, public relations efforts, and potential legal ramifications, the stakes are high. Early detection can mitigate these costs.
Examples of Early Detection
- Unusual Network Traffic: A sudden spike in network traffic, especially during off-peak hours, can be indicative of a botnet communicating with its C&C server.
- Device Performance: If a device suddenly slows down or behaves erratically, it might be executing commands from a bot herder.
- Suspicious IP Addresses: Regularly monitoring and analyzing logs can help identify communication with known malicious IP addresses.
Tools and Strategies for Effective Botnet Detection
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. Advanced IDS solutions can even use machine learning to identify new, previously unknown threats.
- Botnet Detection Software: Specialized software solutions are designed to detect botnet activity specifically. They often employ signature-based detection, behavioral analysis, and heuristics to identify potential threats.
- Traffic Analysis: By regularly analyzing network traffic, organizations can identify patterns consistent with botnet activity. This includes monitoring for repeated communication with known malicious IP addresses or unusual data transfer patterns.
- Sandboxing: This involves running suspicious files or software in a controlled environment separate from the main network. If the file exhibits botnet-like behavior in the sandbox, it can be safely quarantined and analyzed.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: These platforms aggregate data from various sources, providing organizations with up-to-date information on known threats, including botnets. By staying informed, organizations can proactively defend against known botnet strains.
In the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, botnets stand out due to their potential for widespread damage. However, with the right tools, strategies, and a proactive approach, organizations can effectively detect and combat these invisible threats. Early detection isn’t just a strategy; it’s the first line of defense in the battle against botnets.
Challenges in Botnet Detection
The digital cat-and-mouse game between cybersecurity professionals and cybercriminals is relentless. As detection methods become more advanced, so too do the evasion techniques employed by botnets. These sophisticated methods present significant challenges in botnet detection, making it a continuous battle for those tasked with safeguarding digital assets.
Sophisticated Evasion Techniques
- Domain Generation Algorithms (DGAs): Botnets often use DGAs to dynamically generate a large number of domain names. This allows the botnet’s C&C servers to frequently change their location, making them harder to track and shut down. Example: The Conficker worm, one of the most widespread botnets, used DGAs to generate 50,000 domain names daily, making it incredibly challenging for researchers to predict its next move.
- Fast Flux: This technique involves rapidly changing the IP addresses associated with a domain name, effectively moving the botnet’s C&C server around and making it difficult to pinpoint. Example: The Storm Worm botnet employed fast flux to hide its C&C servers, using a vast network of compromised machines to distribute the responsibility of hosting the malicious domains.
- Encrypted Communication: By encrypting the communication between the bot and the C&C server, botnets can hide their malicious activities within seemingly normal traffic, making detection challenging. Example: The Zeus botnet, known for stealing banking credentials, used encrypted communication to transmit stolen data, ensuring that even if traffic was intercepted, it would be unreadable.
The Role of IoT Devices in Botnet Challenges
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has added another layer of complexity to the botnet landscape. These devices, ranging from smart thermostats to security cameras, often lack robust security measures, making them prime targets for botnet recruitment.
- Vulnerability Due to Default Credentials: Many IoT devices come with default usernames and passwords, which users often neglect to change. This makes them easy targets for botnets. Example: The Mirai botnet exploited devices with default credentials, amassing a vast army of IoT devices to launch one of the largest DDoS attacks in history.
- Lack of Software Updates: Unlike computers and smartphones, IoT devices often don’t receive regular software updates, leaving them vulnerable to known exploits. Example: Smart fridges, which might not receive as frequent software updates as other devices, could be left vulnerable to known security flaws, allowing them to be co-opted into a botnet.
- Diverse Ecosystem: The vast array of manufacturers and the lack of standardization in the IoT ecosystem mean that vulnerabilities in one device might not be present in another, making it challenging to devise a one-size-fits-all defense strategy. Example: A vulnerability in a specific brand of smart light bulbs might not affect another brand, requiring different detection and mitigation strategies.
In conclusion, the challenges in botnet detection are multifaceted, stemming from the sophisticated evasion techniques employed by botnets and the vulnerabilities inherent in the burgeoning IoT landscape. As the digital world continues to evolve, so too will the challenges, necessitating continuous vigilance and adaptation from cybersecurity professionals.
Modern Tools for Detecting Botnet Activity
In the dynamic world of cybersecurity, the significance of staying a step ahead of threats cannot be overstated. Botnets, with their increasing complexity, have underscored the importance of having advanced detection tools. These modern tools are engineered to offer in-depth insights into network traffic, pinpoint unusual patterns, and facilitate real-time monitoring, ensuring timely detection and mitigation of threats.
When considering a botnet detection tool, it’s imperative to focus on the following key features:
- Network Traffic Analysis: This evaluates the data packets traversing a network. By examining this traffic, the tool can discern patterns indicative of botnet activity, such as consistent communication with a specific IP or unusual data transfers.
- Behavioral Analytics: Moving beyond just known threat signatures, behavioral analytics understands the standard behavior of a network and its devices. Any deviation from this norm triggers an alert, making it effective against novel or evolving threats.
- Threat Intelligence: This encompasses the gathering and analysis of data about emerging threats. Tools equipped with this feature can preemptively defend against fresh botnet attacks by staying updated with the latest threat intelligence.
- Real-time Monitoring: Immediate detection and mitigation are facilitated by tools that monitor network activity in real-time, ensuring any suspicious activity is instantly flagged.
- IoT Device Monitoring: The surge in Internet of Things (IoT) devices has introduced new vulnerabilities. Tools capable of monitoring these devices are invaluable, given the often-lacking security features of these devices.
Botnet Solutions
Here’s a brief overview of some of the top botnet detection tools available in 2023:
- Snort: An open-source tool known for its robust network traffic analysis and behavioral analytics capabilities. It’s a favorite among many IT professionals for its versatility and community support.
- Bro/Zeek: Offers both network traffic analysis and behavioral analytics. It’s scalable, making it suitable for businesses of various sizes.
- Darktrace: A leader in the realm of threat intelligence, Darktrace uses AI to provide real-time threat detection and autonomous response.
- Splunk: Known for its real-time monitoring capabilities, Splunk offers behavioral analytics and has a user-friendly interface, making it a popular choice for many organizations.
- Cisco Stealthwatch: This tool stands out for its IoT device monitoring feature. Alongside, it offers real-time monitoring, ensuring comprehensive network security.
| Tool | Features | Price | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snort | Network Traffic Analysis, Behavioral Analytics | Open Source | Snort Website |
| Bro/Zeek | Network Traffic Analysis, Behavioral Analytics | Varies by Size | Zeek Website |
| Darktrace | Network Traffic Analysis, Threat Intelligence | Contact for Pricing | Darktrace Website |
| Splunk | Real-time Monitoring, Behavioral Analytics | Varies by Usage | Splunk Website |
| Cisco Stealthwatch | IoT Device Monitoring, Real-time Monitoring | Contact for Pricing | Cisco Website |
In conclusion, the right botnet detection tool can significantly bolster an organization’s cybersecurity posture. By understanding the pivotal features and comparing the leading tools in the market, businesses can make well-informed decisions to fortify their networks.
Real-world Case: The DDoS Attack on a Financial Institution
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks have long been a menace in the cybersecurity landscape. However, the recent attack on a prominent financial institution has brought to light the evolving sophistication and scale of such threats, especially when orchestrated using botnets.
The Role of Botnets
In this particular attack, a massive botnet was deployed, comprising thousands of compromised devices, ranging from personal computers to Internet of Things (IoT) devices. These devices were remotely controlled by attackers to flood the financial institution’s servers with an overwhelming amount of traffic. The sheer volume of requests paralyzed the institution’s online services, rendering them inaccessible to legitimate users.
The botnet’s distributed nature made it challenging to pinpoint the origin of the attack. Each device in the botnet acted as an individual attacker, making traditional defense mechanisms, like blocking a specific IP, ineffective. The scale and coordination of the attack were a testament to the power and danger posed by botnets in executing large-scale DDoS attacks.
Lessons Learned
- Preparedness is Key: The financial institution, despite its robust IT infrastructure, was caught off-guard by the scale of the attack. This incident underscores the importance of regular stress testing and scenario planning to gauge and improve response to such large-scale threats.
- Diversified Defense: Relying on a single defense mechanism, such as IP blocking, is insufficient. A multi-layered defense strategy, incorporating both hardware and software solutions, is crucial to mitigate the diverse threats posed by botnets.
- Real-time Monitoring: The rapid detection of unusual spikes in traffic can be a lifesaver. Real-time monitoring tools can provide early warnings, allowing IT teams to take swift action before the situation escalates.
- Collaboration is Crucial: Sharing threat intelligence with other organizations and joining hands with cybersecurity firms can provide insights into emerging threats and best practices to counter them.
Preventive Measures
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploying IDS can help in identifying unusual patterns in network traffic, providing an early warning system against potential DDoS attacks.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAF): WAFs can filter out malicious traffic, ensuring that only legitimate requests reach the servers.
- Traffic Analysis: Regularly analyzing network traffic can help in identifying potential threats and compromised devices within a network.
- Regular Updates: Keeping all devices, especially IoT devices, updated with the latest security patches can prevent them from becoming part of a botnet.
- Educate and Train: Regular training sessions for IT personnel on the latest threats and countermeasures can go a long way in bolstering an organization’s defense mechanisms.
In conclusion, the DDoS attack on the financial institution serves as a stark reminder of the ever-present threats in the digital realm. While botnets continue to be a formidable tool in the hands of attackers, with the right preventive measures and a proactive approach, organizations can safeguard themselves against such large-scale attacks.
Empowering Small Businesses: Tailored Strategies for Botnet Detection
Small businesses form the backbone of many economies, driving innovation and providing employment to millions. However, when it comes to cybersecurity, they often find themselves in a unique predicament. With limited resources, they are expected to fend off threats that even large corporations struggle with. Botnets, with their evolving sophistication, pose a significant threat to these businesses. But with tailored strategies and a proactive approach, small businesses can effectively counter these threats.
Unique Challenges Faced by Small Businesses
- Limited IT Budget: Unlike large corporations, small businesses often operate on tight budgets, making it challenging to invest in advanced cybersecurity solutions.
- Lack of Dedicated IT Personnel: Many small businesses do not have a dedicated IT team, relying instead on a few individuals or external agencies to manage their IT needs.
- Diverse IT Infrastructure: With a mix of legacy systems and new technologies, small businesses often have a patchwork of IT solutions, making them vulnerable to threats.
- Lack of Awareness: Due to the focus on core business operations, cybersecurity often takes a backseat, leading to a lack of awareness about emerging threats.
Customized Solutions and Strategies For Small Businesses
- Education and Training: Investing in regular training sessions can empower employees to recognize and report potential threats. Workshops focusing on the basics of botnet detection and prevention can be invaluable.
- Leverage Cloud Solutions: Cloud-based cybersecurity solutions offer advanced protection without the need for significant upfront investment. These solutions are scalable, ensuring that as the business grows, the security measures grow with it.
- Regular Audits: Periodic security audits can help identify vulnerabilities in the IT infrastructure. By addressing these vulnerabilities proactively, businesses can prevent potential breaches.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA for accessing business systems can add an additional layer of security, ensuring that even if passwords are compromised, unauthorized access is prevented.
- Tailored Threat Intelligence: Subscribing to threat intelligence services tailored for small businesses can provide insights into specific threats targeting this demographic. This allows businesses to take preemptive measures.
- Collaboration and Community: Joining local or online cybersecurity communities can provide small businesses with access to shared resources, best practices, and collective threat intelligence.
- Backup and Recovery: Ensuring regular backups of critical business data and having a robust recovery plan in place can mitigate the impact of potential breaches.
In conclusion, while small businesses face unique challenges in the realm of cybersecurity, with tailored strategies and a proactive approach, they can effectively safeguard themselves against botnets and other threats. Empowering these businesses with the right tools and knowledge is crucial in ensuring a secure digital future.
Conclusion: Staying One Step Ahead
The digital landscape of today is fraught with challenges, and botnets represent one of the most insidious threats. For small businesses, the stakes are even higher, given the limited resources at their disposal. However, with awareness, education, and the right tools, these threats can be effectively managed.
The visual representation above outlines the crucial steps to take if one suspects a botnet infection:
- 1. Suspect Botnet Infection: Recognizing unusual behavior in your network or devices.
- 2. Isolate Affected Devices: Preventing the potential spread of the infection.
- 3. Scan for Malware: Using reliable tools to detect threats.
- 4. Remove Detected Threats: Ensuring complete removal of malware.
- 5. Update All Software & Firmware: Keeping systems up-to-date.
- 6. Change All Passwords: Securing all accounts.
- 7. Monitor Network Traffic: Watching for unusual activity.
- 8. Educate & Train Employees: Keeping the team informed.
- 9. Implement Multi-factor Authentication: Adding an extra layer of security.
- 10. Regularly Backup Data: Safeguarding critical data.
The journey to cybersecurity is not a destination but a continuous process of adaptation and learning. By understanding the nature of botnets, their operation, and the tools available for detection, small businesses can fortify their defenses and navigate the digital realm with confidence. The key lies in proactive measures, continuous education, and leveraging the power of community and collaboration. In the face of evolving threats, knowledge remains our most potent weapon.
The post Botnet Detection in 2023: What You’re Missing Out On! appeared first on Endpoint Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Endpoint Security authored by Michael Toback. Read the original post at: https://smallbizepp.com/botnet-detection/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=botnet-detection