What is Reverse Proxy, How Does It Works, and What are Its Benefits?
What is a Reverse Proxy?
A reverse proxy is a server that sits between the client and the origin server. It accepts requests from clients and forwards them to the appropriate server. It also receives responses from the server and sends them back to the client.
A reverse proxy is an essential component of web application infrastructure, providing a layer of abstraction between clients and origin servers to help optimize traffic routing and improve performance and security.
How Does a Reverse Proxy Work?
Reverse proxies work by sitting in front of the origin server and acting as an intermediary between clients and the server.
Here’s a more detailed overview of how a reverse proxy works in front of an origin server:
- A client sends a request to the web application by entering a URL or clicking a link.
- The reverse proxy intercepts the request, which examines the request and determines which backend server should handle the request.
- The reverse proxy forwards the request to the origin server, which processes the request and generates a response.
- The response is sent back to the reverse proxy, which examines the response and forwards it to the client.
Reverse proxies can also perform other tasks in front of the origin server, such as load balancing, SSL termination, and caching. These features can help to improve performance, scalability, and security for web applications.
In addition, they can be configured to route traffic based on different criteria, such as geographic location, user agent, or cookie value. This helps optimize traffic routing and improve the user experience for clients.
Forward Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy – What are the Differences?
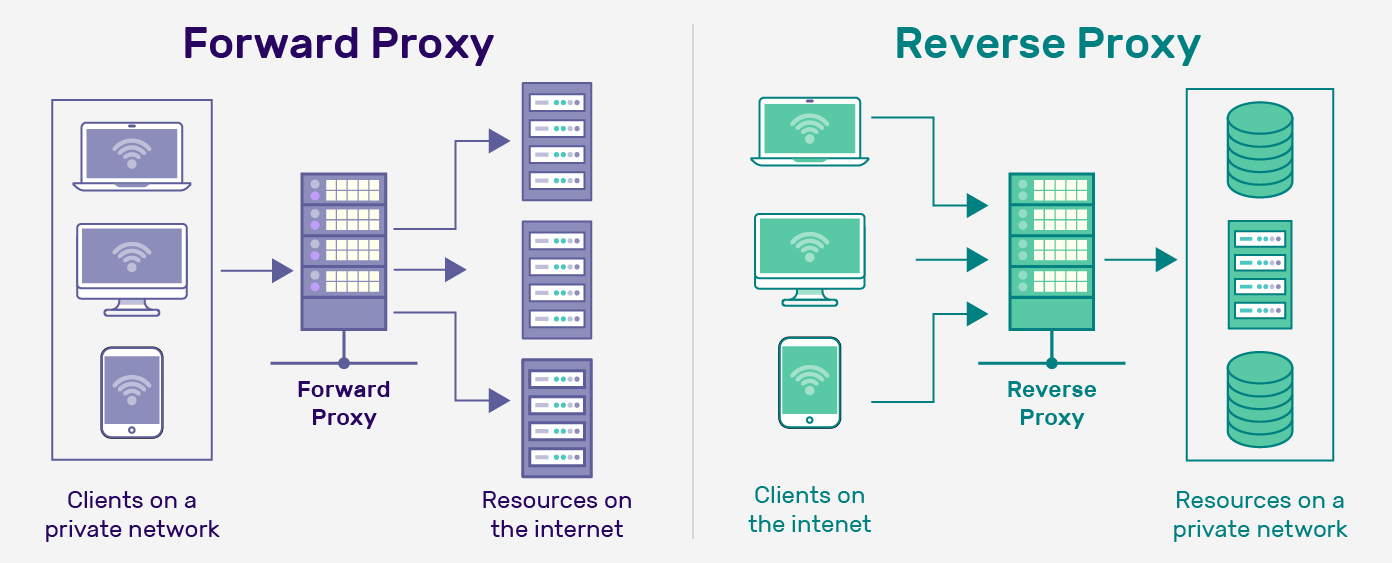
A forward proxy is the designated exit point for subnet users seeking to connect with resources outside their private network. In contrast, a reverse proxy is the entry point for external systems to access resources within a private subnet.
The primary difference between forward and reverse proxies is their position in the network architecture. A forward proxy sits between a client and the internet, while a reverse proxy sits between a client and a server.
Another key difference is their purpose. A forward proxy is primarily used to provide privacy to the client and bypass network restrictions. In contrast, a reverse proxy is used mainly to improve the server’s performance, security, and scalability.
Individuals typically use forward proxies to access restricted content, while organizations use reverse proxies to optimize their web applications.
What are the Benefits of Reverse Proxy?
1. Load Balancing
Load balancing refers to distributing incoming client requests across multiple backend servers. When a client sends a request to a reverse proxy, the reverse proxy can decide which backend server should handle the request based on various factors, such as server availability, server load, or geographic location.
Load balancing helps improve performance and scalability by allowing multiple servers to handle incoming traffic. This helps distribute the load evenly among the servers, preventing any server from overloading, slowing down, or failing.
2. Caching
Reverse proxies can cache frequently accessed content and serve it directly to clients, reducing the load on backend servers and improving response times.
3. SSL Termination
Reverse proxies can handle SSL encryption and decryption, allowing clients to connect securely to the backend server without the server having to take the overhead of SSL.
4. Threat Prevention
Reverse proxies can help protect backend servers from malicious traffic by filtering requests and blocking suspicious traffic. By blocking or rate-limiting suspicious requests, reverse proxies can prevent servers from being overwhelmed and keep the application running smoothly. It can also mask the server’s IP address, making it harder for attackers to launch a DDoS attack.
5. Scalability
A reverse proxy can add or remove servers dynamically, making it easy to scale web applications. This feature allows administrators to handle traffic spikes or increase capacity without downtime.
6. Compression
Reverse proxies can compress and optimize content before sending it to clients, reducing bandwidth usage and improving performance.
7. Routing
Reverse proxies can route requests to specific backend servers based on various criteria, such as URL path, HTTP headers, or geographic location.
8. Monitoring and Logging
Reverse proxies can monitor traffic and log activity, providing insights into usage patterns and potential security threats.
9. Flexibility
A reverse proxy can modify requests and responses in real-time. This feature allows administrators to implement complex routing rules, rewrite URLs, and add or remove headers.
Is WAF a Reverse Proxy?
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) can be considered a type of reverse proxy. By intercepting traffic before it reaches the server, the WAF can help prevent malicious requests from reaching the origin server.
WAF can help safeguard a company’s web applications by mitigating application layer cyber-attacks such as SQL-Injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), Session Hijacking, and OWASP top 10 vulnerability threats.
Indusface AppTrana uses a set of policies to filter malicious traffics without slowing down the web service.
While ensuring zero false positives, the WAF can protect web servers against all known vulnerabilities and zero-day attacks. It also serves as a load balancer to distribute traffic and ensure application and API stability.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security updates. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn
The post What is Reverse Proxy, How Does It Works, and What are Its Benefits? appeared first on Indusface.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Indusface authored by Vinugayathri Chinnasamy. Read the original post at: https://www.indusface.com/blog/what-is-reverse-proxy/




