The Human Factor in Threat Simulation: Testing Employee Awareness and Training Effectiveness
As businesses increasingly rely on technology to store and manage sensitive information, the risks associated with cyber attacks continue to rise. While many companies invest in top-of-the-line security software and hardware, the reality is that one of the most significant vulnerabilities often comes from within the organization itself: the human factor. Employees who are not properly trained on cybersecurity best practices can inadvertently put the entire organization at risk. This is why it is crucial to incorporate the human factor into threat simulation exercises, including testing employee awareness and training effectiveness.
In this blog post, we will explore why it is essential to incorporate the human factor into threat simulation exercises, as well as best practices for testing employee awareness and training effectiveness.
Why Incorporate the Human Factor?
Threat simulation exercises are an essential component of any comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. By simulating real-world attack scenarios, organizations can identify potential vulnerabilities and train employees on best practices for avoiding and responding to cyber threats. However, it is not enough to focus solely on technological vulnerabilities.
Many cyber attacks exploit human weaknesses, such as opening suspicious email attachments or clicking on phishing links.
Here are some of the latest stats that involve human factors:
- The average cost of a data breach is now $4.24 million. This is up from $3.86 million in 2022.
- The most common way that hackers gain access to a network is through a phishing attack. Phishing attacks are emails that appear to be from a legitimate source, such as a bank or credit card company. The emails often contain a link that, when clicked, takes the victim to a fake website that looks like the real website. Once the victim enters their personal information on the fake website, the hacker can steal it.
- Human error is the leading cause of data breaches. In fact, a study by the Ponemon Institute found that human error is responsible for 88% of data breaches.
- Employees are often the weakest link in a company’s security defenses. This is because employees are often not trained on how to spot phishing attacks or other types of cyberattacks.
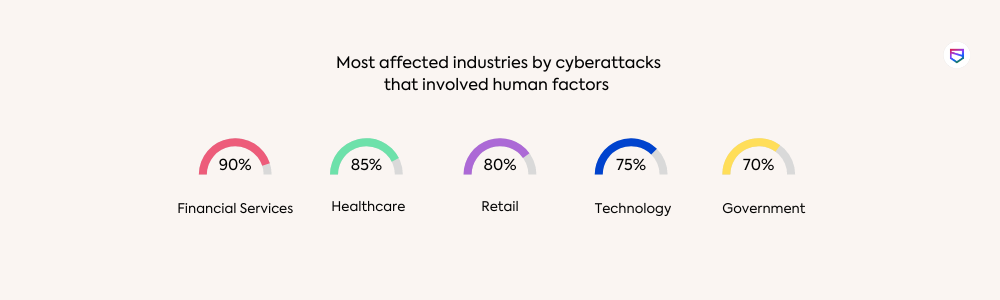
By training employees to recognize these common tactics, organizations can reduce the likelihood of a successful attack.
Additionally, employees are often the first line of defense in identifying and reporting potential security incidents. By improving employee awareness and response capabilities, organizations can enhance their overall security posture and reduce the risk of a major breach.
Testing Employee Awareness and Training Effectiveness
To effectively test employee awareness and training effectiveness, threat simulation exercises should be designed to mimic real-world scenarios. This can include sending out simulated phishing emails, conducting social engineering tests, or even staging physical security breaches.
The results of these exercises can be used to identify areas for improvement in employee training and security protocols. Additionally, these exercises can be used to demonstrate the importance of cybersecurity to employees and encourage a culture of security awareness throughout the organization.
Tips for an Effective Threat Simulation Exercise
When designing a threat simulation exercise, keep the following tips in mind:
- Make it realistic: Ensure the exercise simulates a real-world scenario to test employee awareness and response accurately.
- Involve all employees: Regardless of their position, every employee should be involved in the exercise to ensure that the organization is fully prepared.
- Provide immediate feedback: Employees should receive feedback immediately after the exercise to reinforce positive behaviors and identify areas for improvement.
- Follow-up with training: After the exercise, employees should receive additional training on the best practices for avoiding and responding to cyber threats.
Some of the latest stats on threat simulation exercises
- In 2022, 85% of organizations that conducted threat simulation exercises found that they had at least one security gap. This is up from 75% in 2021.
- The average cost of a data breach caused by a security gap that was identified in a threat simulation exercise is $2.5 million.
- Organizations that conduct threat simulation exercises are more likely to be prepared for a cyberattack. A study by the SANS Institute found that organizations that conduct threat simulation exercises are 60% more likely to be prepared for a cyberattack than organizations that do not.
Conclusion
Incorporating the human factor into threat simulation exercises is an essential component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. By identifying vulnerabilities and training employees to recognize and respond to cyber threats, organizations can reduce the risk of a security breach and protect their valuable assets.
By following best practices for testing employee awareness and training effectiveness, organizations can ensure that their employees are fully prepared to prevent and respond to cyber-attacks.
Recommended Reading
7+ Major Reasons to Hire a Red Team to Harden Your App Sec
Red Team Assessment versus Penetration Testing
Social Engineering Attacks – Manipulating your thoughts to fall in trap
The post The Human Factor in Threat Simulation: Testing Employee Awareness and Training Effectiveness appeared first on WeSecureApp :: Simplifying Enterprise Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from WeSecureApp :: Simplifying Enterprise Security authored by Naimisha. Read the original post at: https://wesecureapp.com/blog/the-human-factor-in-threat-simulation-testing-employee-awareness-and-training-effectiveness/





